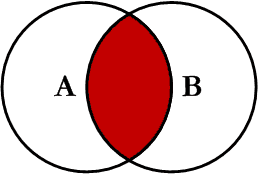
- SQL Joins are used to combine or join rows from the two or more tables.
Joining two tables.
Types of joins:
1.Inner join.2.Left outer join.
3.Right outer join.
4.Full outer join.
5.Self join
Types of joins
Inner join:
- The INNER JOIN keyword selects all rows from both tables as long as there is a match between the columns in both tables.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
Left outer join:
- The LEFT JOIN keyword returns all rows from the left table (table1), with the matching rows in the right table (table2). The result is NULL in the right side when there is no match.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
LEFT JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
Right outer join:
- The RIGHT JOIN keyword returns all rows from the right table (table2), with the matching rows in the left table (table1). The result is NULL in the left side when there is no match.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
RIGHT JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
Full outer join:
- The FULL OUTER JOIN keyword combines the result of both LEFT and RIGHT joins.
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table1
FULL OUTER JOIN table2
ON table1.column_name=table2.column_name;
Cross join or Cartesian join:
- The SQL CROSS JOIN produces a result set which is the number of rows in the first table multiplied by the number of rows in the second table, if no WHERE clause is used along with CROSS JOIN. This kind of result is called as Cartesian Product.
SELECT *from table1 CROSS JOIN table2.